At the conclusion of the lecture, the leaner should be able to:
- Perform initial assessment of a patient having an airway difficulty.
- Recognize signs and symptoms of airway obstruction and its severity.
- Know adequate work-ups to identify the site of airway problem.
- Know normal and abnormal airway anatomy seen on a flexible laryngoscopy
- Learn initial, non-invasive medical treatment options for an airway patient.
- Supplemental oxygen
- Racemic epinephrine
- Corticosteroids
- Antibiotics
- Antihistamines
- Heliox
- CPAP/BiPAP
- Learn invasive methods of securing airway.
- Bag-Valve-Mask ventilation
- Nasopharyngeal airway
- Oropharyngeal airway
- Orotracheal intubation
- Laryngeal mask airway
- Learn surgical options of securing airway
- Flexible Fiberoptic Intubation
- Benefits of transnasal approach vs. transoral approach
- Direct laryngoscopic intubation
- Telescopic rigid bronchoscopy with ventilation
- Cricothyroidotomy
- Emergent tracheostomy
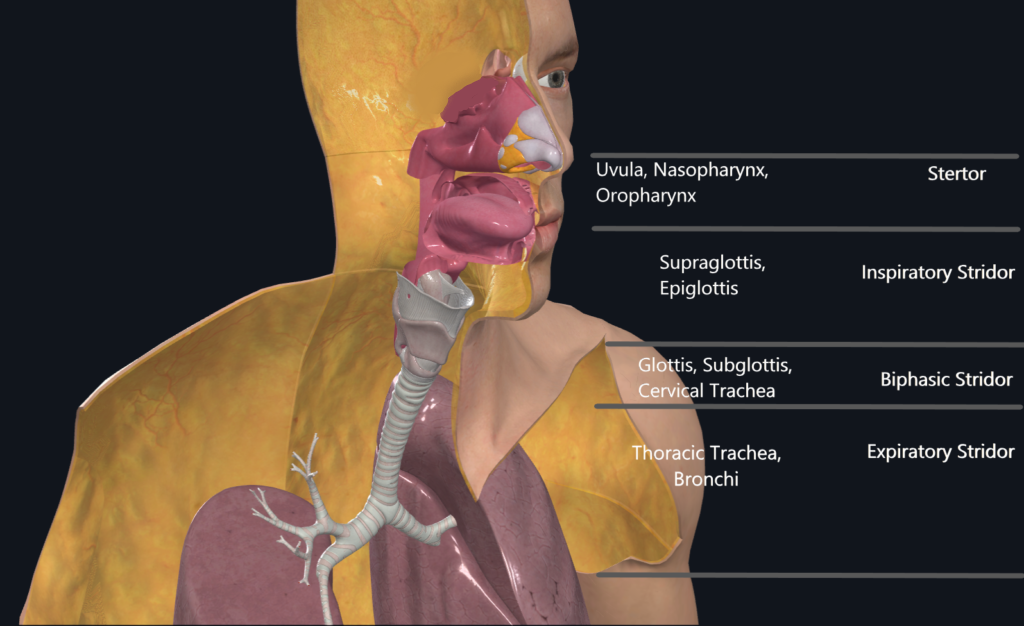
Airway Signs to Diagnose Site of Airway Obstruction
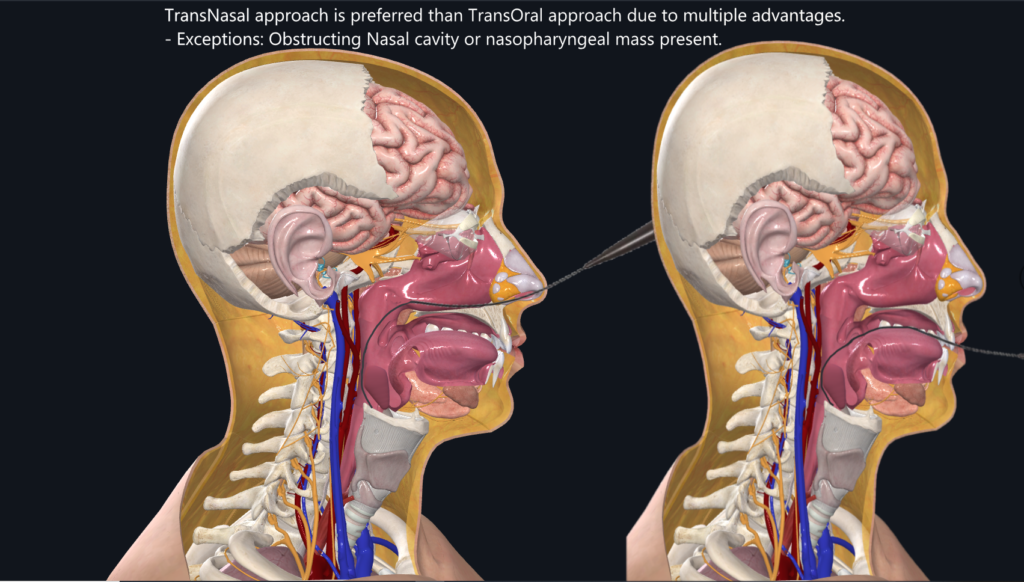
Transnasal Intubation is typically easier than Transoral Intubation.
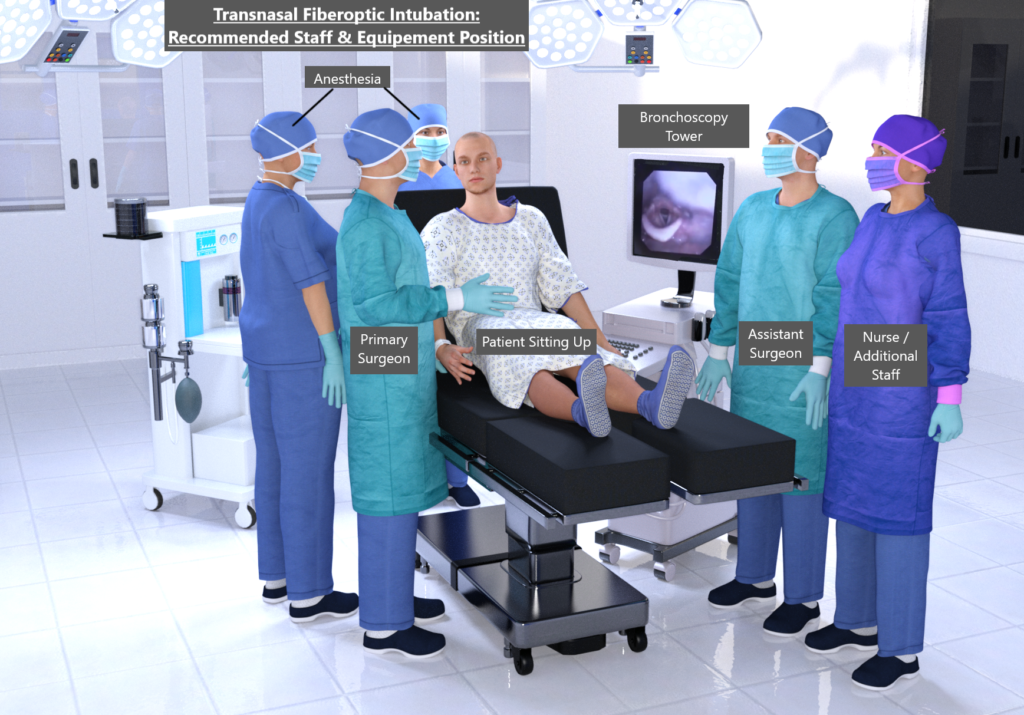
Preferred Staff & Equipment Positioning for Transnasal Fiberoptic Intubation
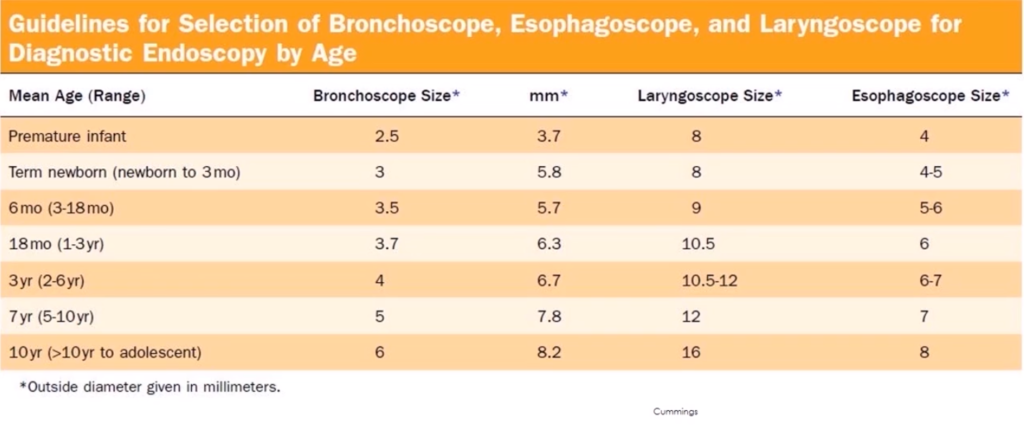
Pediatric Bronchoscope Sizing
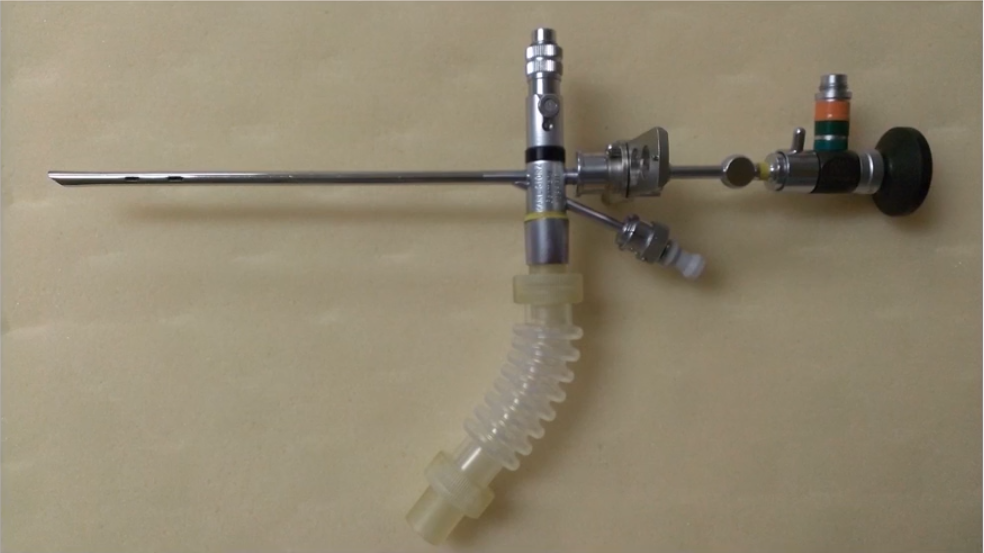
Assembled Bronchoscope





