By Benjamin Wie MD, Thomas S. Lee MD, FACS
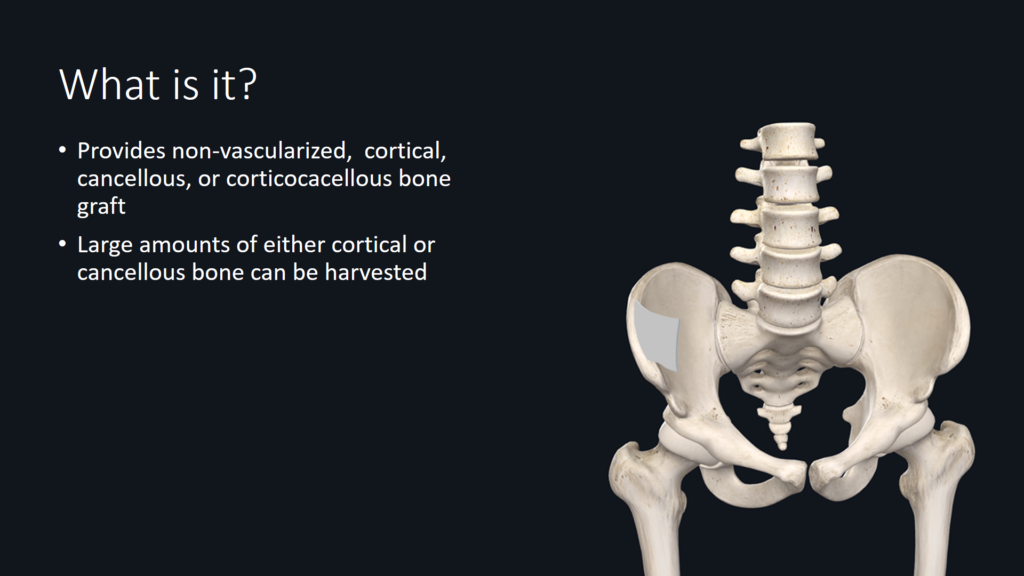
What is iliac bone graft?


Clinical Indications in Head & Neck Regions
Mandible Reconstruction
- Posterior Segmental Defect Greater than 6cm (located posterior/lateral to mental foramen)
- If Anterior Defect (Medial/Central to mental foramen), it may require vascularized free flap reconstruction
- Nonunion Mandible Defect
- Tx: Reconstruction Plate + Autogenous Bone Graft +/- BMP
- Increase vertical height of alveolar bone for Dental Implants
Maxillary Reconstruction
- Orbital Floor Reconstruction after Maxillectomy Defect
- Consider wrapping non-vascularized bone graft in either/combined pericranial flap & temporalis flap to avoid nasal mucosa/mucus contacting the bone graft
- Non-vascularized bone graft can also be wrapped in free flap soft tissue to avoid nasal content contacting the bone graft as it will lead to high rate of infection and hardware failure
- Alveolar Cleft Defect
When to avoid using non-vascularized bone graft?
- Infected wound bed
- Radiated tissue bed
- Prone to saliva or nasal mucus exposure
- Postoperative radiation therapy needed
- Bone Graft will most likely fail if:
- Bone graft is not covered within well vascularized tissue
- Bone graft is exposed to saliva
- Bone graft is within fistula tract
- Bone graft is exposed to nasal mucosa or mucus.
- Bone graft is exposed to air
- Postoperative radiation therapy is need
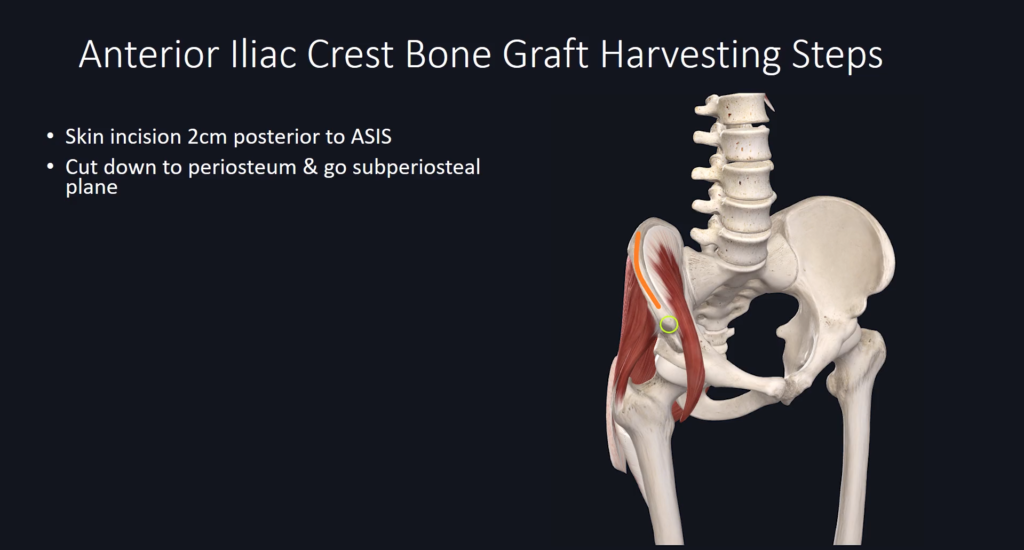
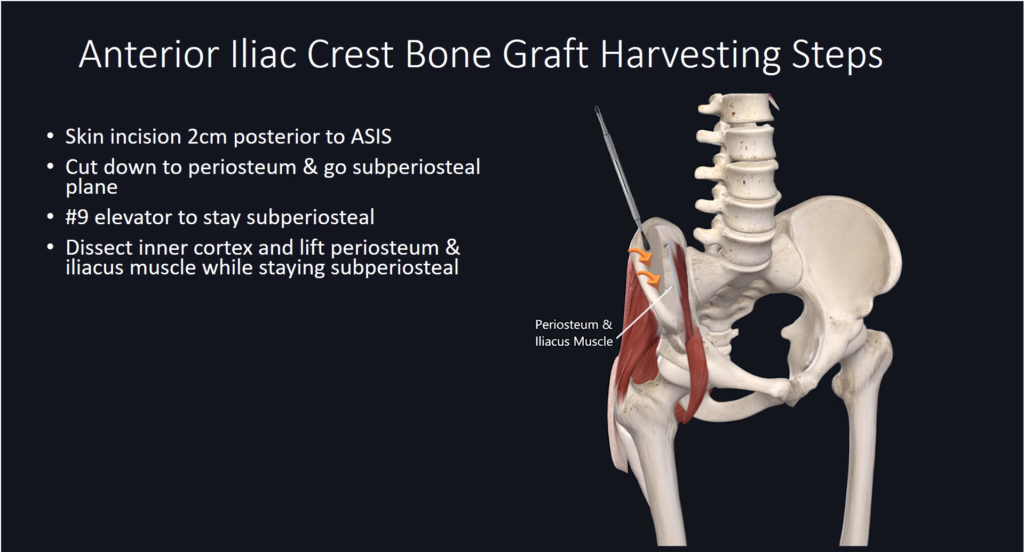
Harvesting Steps Overview
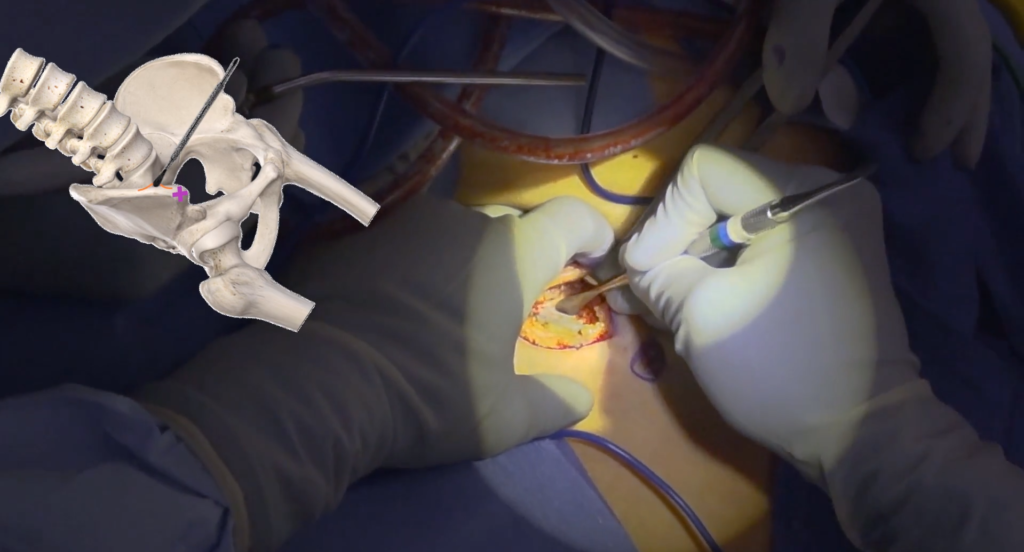
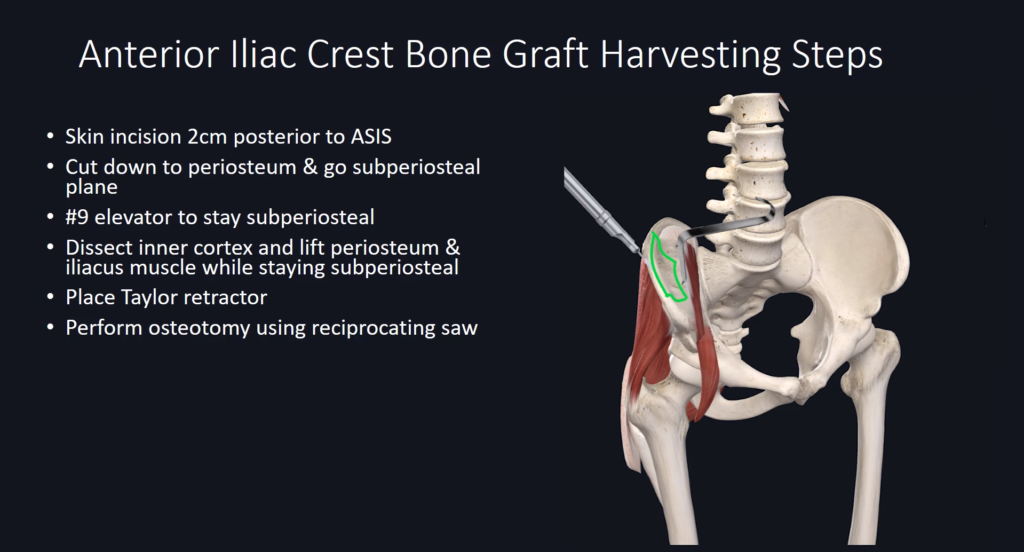
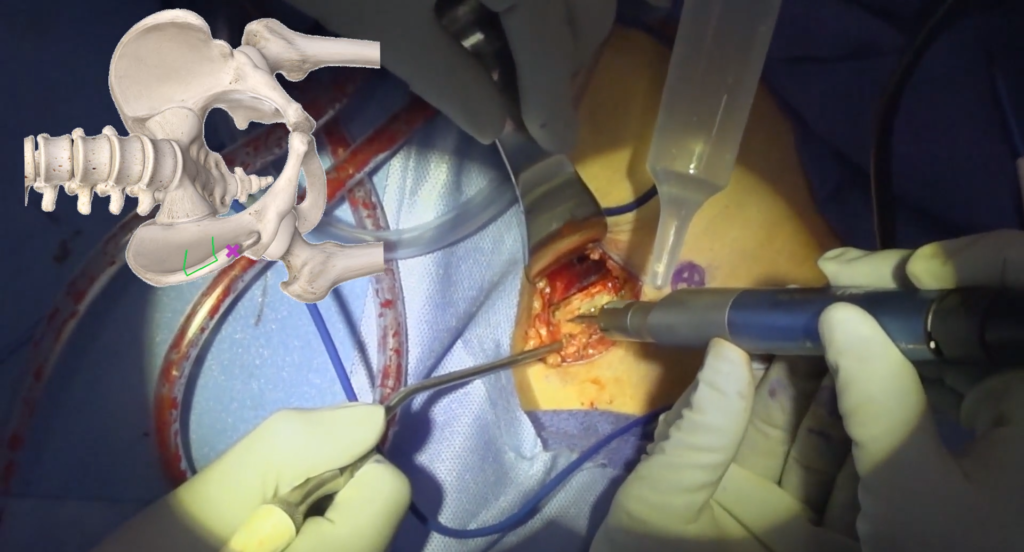
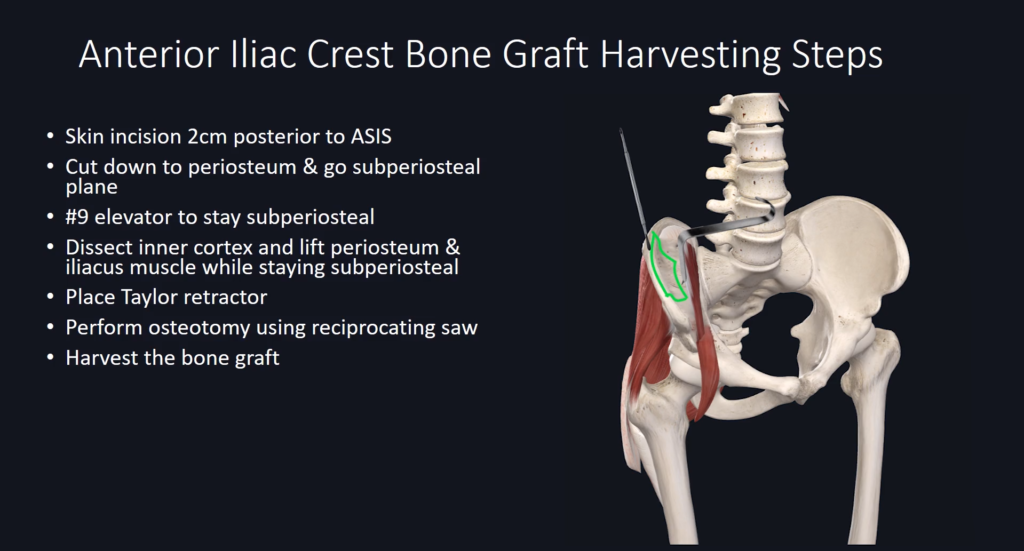
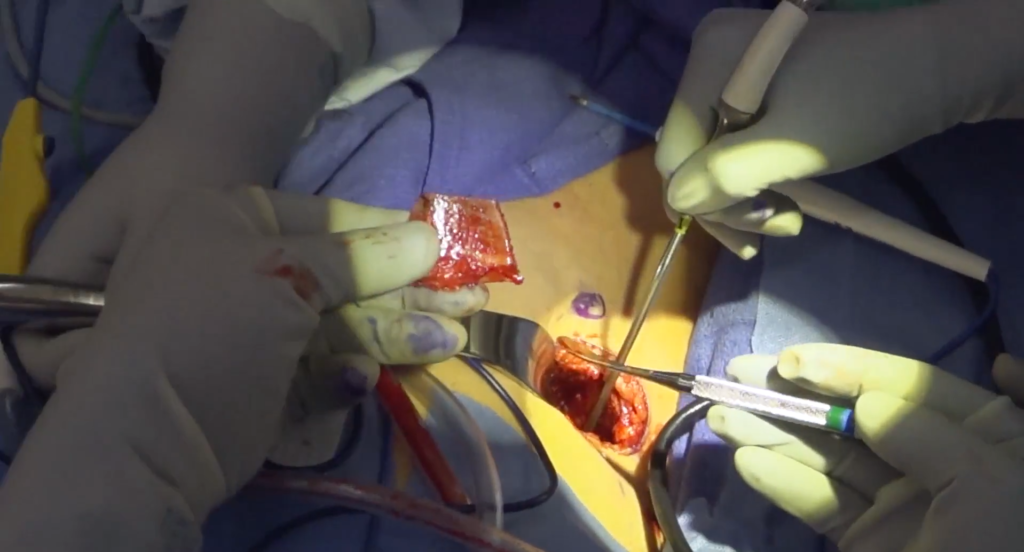
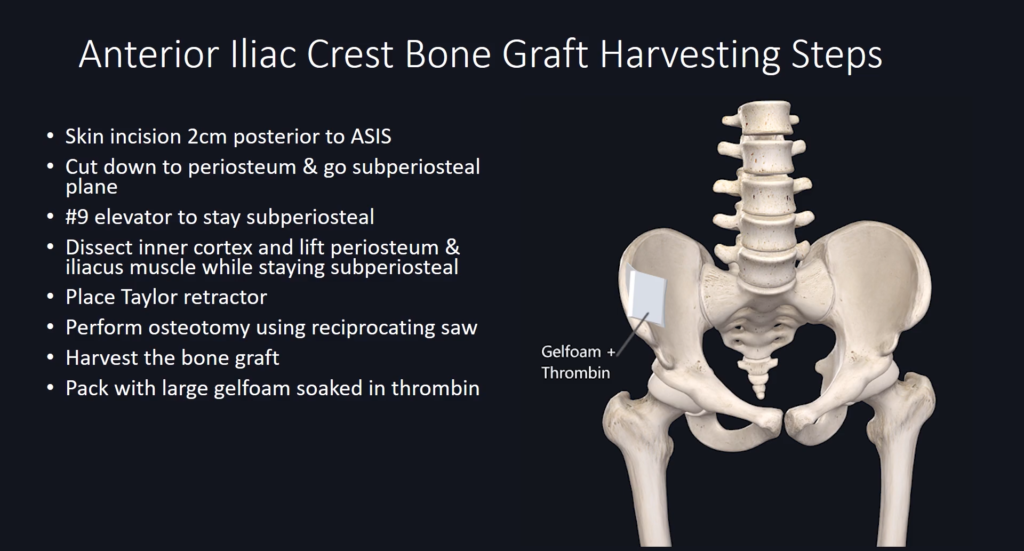
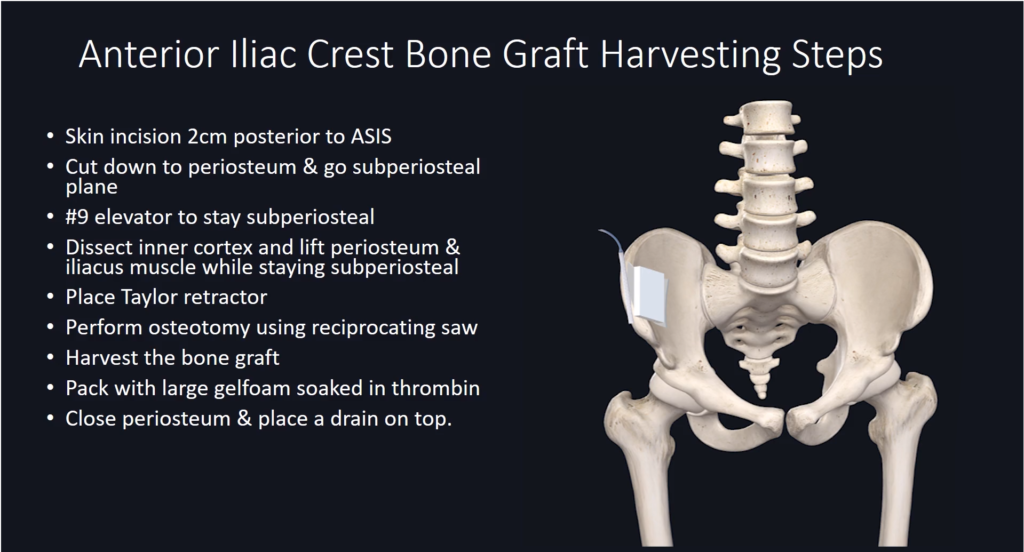
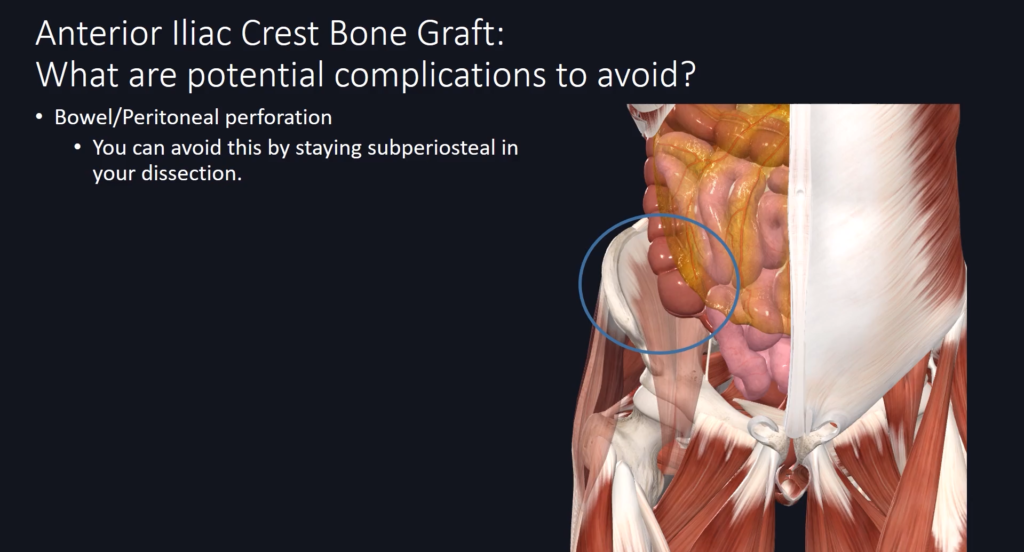
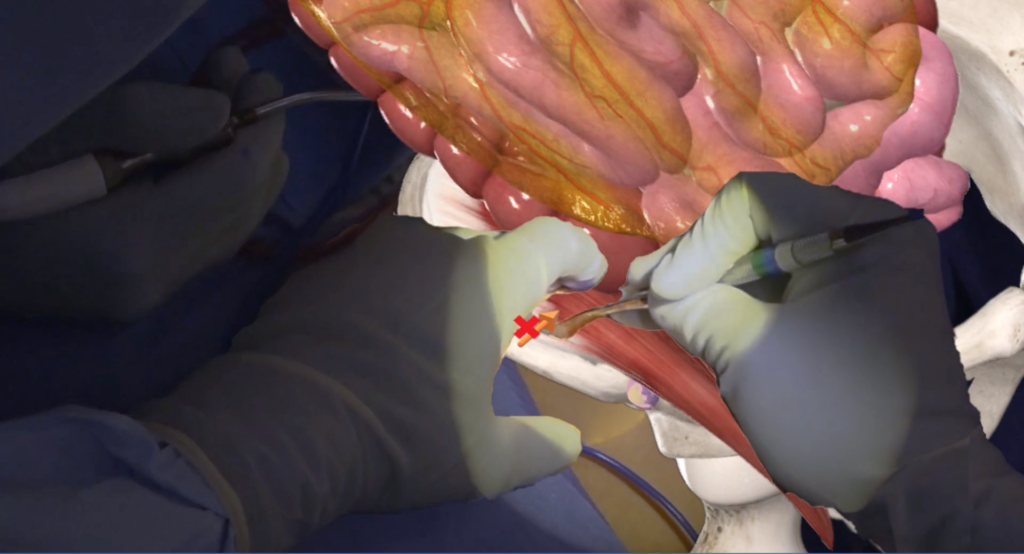
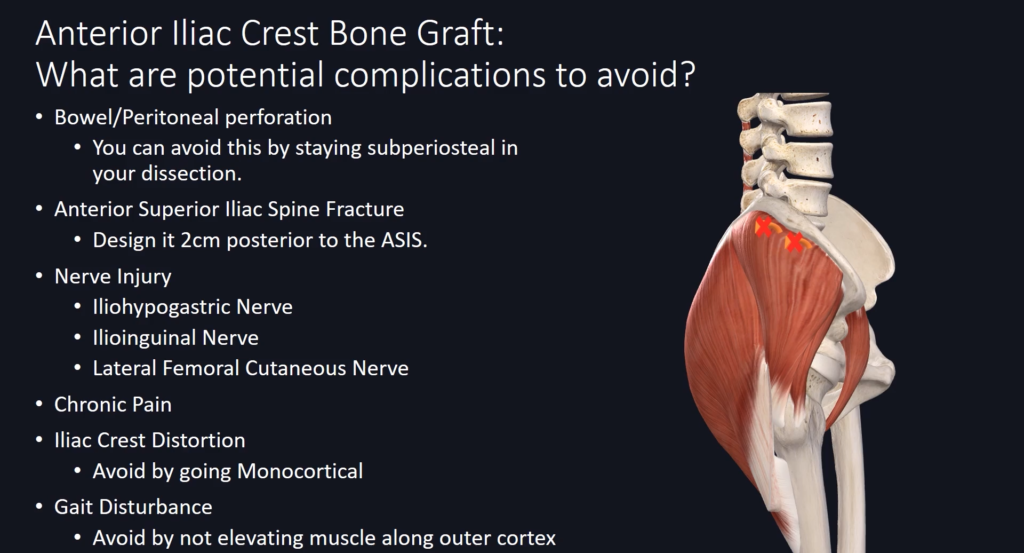
Complications to Avoid During Harvesting